Let’s address the difference between cyber risk and cyber threat
Managing risk and addressing threats in cyber security is a critical aspect of an organisation’s overall security strategy. Essentially organisations need to have a proactive outlook implementing measures to identify and mitigate potential risks and reactive steps to respond to specific threats.
Ultimately organisations need manage their risks as well as their threats so let’s breakdown how they do that:
Risk Management:
Risk management in cyber security involves assessing and addressing potential vulnerabilities and the impact they may have on the organisation. This helps prioritise security efforts and allocate resources effectively. Key steps in risk management include:
Risk Assessment:
- Identify assets: Identify all an organisations’ assets and thus determine what information, systems and resources are most critical.
- Identify threats: Understand the potential threats and vulnerabilities that could affect these assets.
- Risk analysis: Evaluate the likelihood and potential impact of various threats to determine the level of risk associated with each.
- Risk prioritisation: Prioritise risks based on their potential impact and likelihood.
Risk Mitigation:
- Implement security controls: Put in place security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, access controls and more to reduce vulnerabilities.
- Security policies and procedures: Develop and enforce security policies and procedures that address potential risks.
- Training and awareness: Ensure that employees are educated about security best practices and are aware of their role in risk mitigation.
Risk Monitoring and Review:
- Continuously monitor systems and networks for potential vulnerabilities.
- Regularly review and update risk assessments to adapt to changing threat landscapes.
- Report on those risks at Board level.
Threat Management:
Specific and active threats are addressed with threat management, involving detecting, responding to and mitigating these threats.
The threat management key steps are:
Threat Detection:
- Use security tools and technologies (e.g., antivirus, intrusion detection systems, SIEM) to monitor networks and systems for signs of unauthorised access or malicious activity.
- Collect and analyse logs and data to identify potential threats.
Incident Response:
- Develop an incident response plan that outlines how the organisation will react to a cyber security incident.
- Establish an incident response team with defined roles and responsibilities.
- Quickly respond to and contain threats to prevent further damage.
Threat Mitigation:
- Measures must be implemented to remediate the issue once an incident has occurred. This may involve removing malware, patching vulnerabilities and restoring affected systems.
Continuous Improvement:
- After a security incident organisations should conduct a post-incident analysis to understand what went wrong and how to prevent similar incidents in the future.
- Update security measures and policies based on lessons learned from past incidents.
- Understand the what why and when – continuous controls monitoring can help you understand your tech infrastructure and where the improvements need to be made.
So why should a business focus on both mitigating risks as well as dealing with cyber threats?
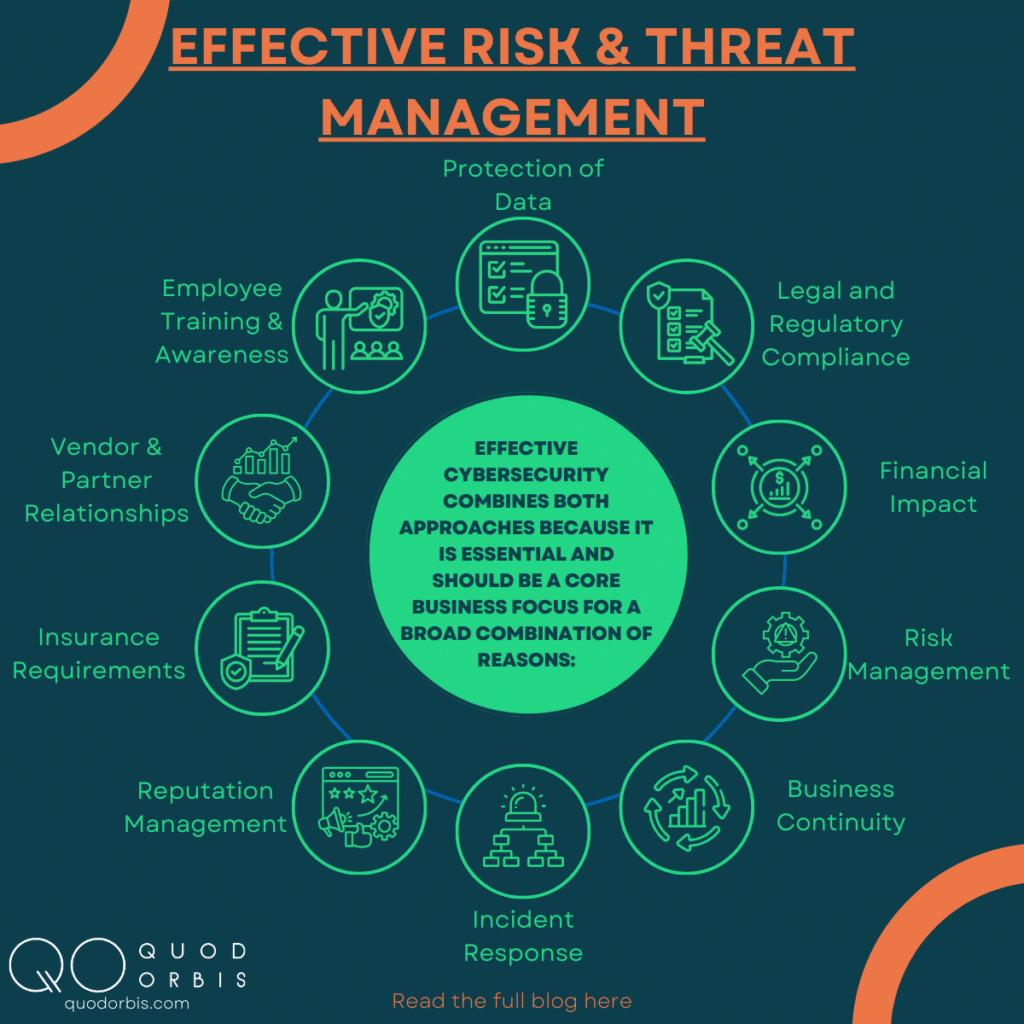
Effective cyber security combines both approaches because it is utterly essential and should be a core business focus for a broad combination of reasons:
- Protection of Data: Any business will have sensitive and confidential data, such as customer information, financial records and intellectual property. The first step is to understand where your assets are that more than likely hold valuable data and understand how to protect it from theft and unauthorised access, developing policies in line with those risks and threats.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Many industries are subject to laws and regulations related to data security and privacy. Having cyber threat and risk procedures in place helps ensure compliance with these legal requirements, reducing the risk of penalties or lawsuits. The next step on from this would be to continuously monitor your regulatory compliance to ensure that you remain compliant, thus reducing your risk.
- Financial Impact: Cyber threats can be costly, leading to financial losses in terms of legal settlements, regulatory fines, business disruption and loss of revenue. Risk procedures help minimise the financial impact of such incidents.
- Risk Management: Cyber threat procedures are an essential component of overall risk management. By identifying potential threats, assessing vulnerabilities, and implementing protective measures, businesses can proactively manage their cyber security risks.
- Business Continuity: Cyber attacks can disrupt operations, affecting a company’s ability to function. Procedures help to minimise downtime, restore services and ensure business continuity in the event of an attack.
- Incident Response: Procedures help guide how an organisation responds to a cyber incident. They outline steps to mitigate the damage, identify the source of the threat and recover from the attack more effectively.
- Reputation Management: A cyber breach can damage a business’s reputation and erode trust with customers, partners and stakeholders. Effective procedures can mitigate these risks and demonstrate a commitment to safeguarding sensitive information.
- Insurance Requirements: Some insurance policies may require businesses to have certain cyber threat and risk procedures in place to qualify for coverage. Having these procedures can be a prerequisite for obtaining cyber insurance. Not only that, but by implementing a continuous monitoring programme assures cyber insurers that you are taking every step necessary to mitigate the risk and reduce the threats to your organisation, therefore potentially reducing your premiums.
- Vendor and Partner Relationships: Businesses often work with vendors and partners and they may share data or access systems. Having procedures in place can be a requirement or a selling point when establishing these relationships.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Last and by no means least is the importance of your employees. By leading from the top and establishing procedures helps educate employees about cyber threats and the role they play in maintaining security. It encourages a culture of vigilance and security awareness within the organisation.
In summary, cyber threat and risk procedures are essential for protecting a business’s sensitive data, complying with regulations, safeguarding its reputation, ensuring business continuity and managing financial and operational risks associated with cyber threats. Proactive measures such as implementing continuous controls monitoring, can help prevent, detect and respond to cyber threats effectively, ultimately contributing to the long-term success of the business.
Would you like to find out more about how our continuous controls monitoring platform provides the holistic “single source of truth” to your Cyber risk, compliance and security posture? Find out more by clicking here